Cardinality ER Diagram Examples – It is believed that the ER Diagram can be a great tool in data mining. This is because it allows users to see complex relationships in a simple format. The fundamentals are the same no matter where you’re working. One of the first steps is to determine “what” your system is. A rectangle is the symbol of the entity and should have plenty of room. Then, you can insert ovals for attributes and connect them with the entity. In the end, leave a space between each rectangle.
Every entity in an ER diagram is referred to as an attribute. The term “attribute” refers to a property or trait or characteristic of an object. In the case of an ER diagram an inventory Item Name is an attribute associated with the organization Inventory Item. The entity may possess any number of attributes it needs, and each attribute may have distinct attributes. For example, a customer’s address may have the following attributes: street number as well as a city and state. They are composite attributes which means there aren’t restrictions on the number of each.
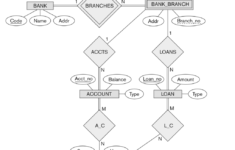
The next phase in analyzing the ER diagram will be to establish the amount of information that each entity holds. The cardinality of an individual is the number of elements that are shared among two different entities. For instance, a client could buy several phones on the same cell phone service while the cell operator maintains multiple phones in only one bill. The ER diagram will make it easier to determine how the entities are connected. In addition, it can help you to determine the type of data that links each entity together.
As the system develops and becomes more complex the ER diagram could become crowded and difficult to understand. The complex nature in an ER diagram demands more precise representation at the micro-level. A well-designed ER diagram can help you comprehend a system in a more thorough manner. It is important to include white space between tables in the ER diagram to ensure that there is no confusion. If you don’t, it’ll be difficult to figure out the connection between two entities.
A person is an object. An entity is a thing or class. An entity can be a person an individual, a city, or an organisation. A weaker entity is one that relies on anotherentity, but lacks the primary attributes. An attribute defines a property of an object. The person in the ER diagram is a noun. As well, the city itself constitutes an entire entity. Therefore, the term “connection” between an entity is an adjective.
The attributes included in an ER diagram must be identified. A teacher entity can have multiple subjects. Student entities can have several subjects. The relationship between two parties is represented by diamond-shaped shapes. The lines are usually marked with verbs. Then, they are described as entities. If a student has doubts over the meaning of an attribute and is unsure of its meaning, the ER diagram will aid in understanding the connection between two different objects.