ER Model Diagram Examples – The ER Diagram can be a fantastic tool to use in data mining. It allows you to show complicated relationships in a straightforward format. The basic steps are the identical wherever you work. The first step is to determine “what” your system is. A rectangle represents the entity and should be given plenty of room. Then, you can insert ovals for attributes and connect them with the entity. In the end, leave a space between rectangles and ovals.
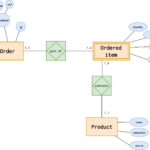
Every entity in one ER diagram is called an attribute. The term “attribute” refers to a property, trait, or characteristic of an entity. In the case in an ER diagram it is an Inventory Item Name is one of the attributes belonging to an inventory Item. The entity could have as many attributes as it needs, and each attribute may have its own specific attributes. For instance, a client’s address may have an address, street number or city. It could also have a state. These are composite attributes and there’s no limit in the amount of each.
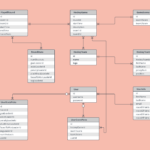
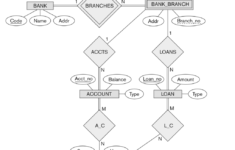
The next step in the process of analyzing the ER diagram will be to define the amount of information each entity has. The primary characteristic of every person is the number of variables that exist in between the two organizations. For instance, a customer might purchase multiple phones using one phone service and the cell phone provider may have many phones with one bill. The ER diagram can help make it easier to recognize the links between the entities. It can also aid in determining what information is the basis of each entity.
As the system develops and becomes more complex The ER diagram may become congested and difficult to comprehend. The complex nature associated with the ER diagram demands more precise representation of the micro-level. A properly designed ER diagram will allow you to understand a system in a more thorough manner. It is important to include white space in between the tables of your ER diagram to avoid confusion. If you don’t, it will be difficult to determine the connection between two entities.
An individual is an entity. An entity is an object or a class. An entity can be an individual an individual, a city, or an institution. A weaker entity is one that is dependent on anotherentity, but lacks the key attributes. An attribute is a description of a characteristic of an object. The person depicted in the ER diagram is an adjective. The city, too, is an entity. The reason why a connection is established between an entity is a noun.
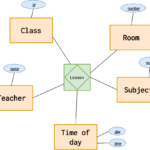
The attributes within the ER diagram must be identified. For instance, a teacher entity could have multiple values for a subject. A student can be a part of multiple subjects. The relationship between two people is illustrated in the form of diamonds. In general, these lines are marked by verbs. Then, they are described as entities. If a student has doubts about the meaning of an attribute or a term, the ER diagram can aid them in understanding the relation between two different objects.