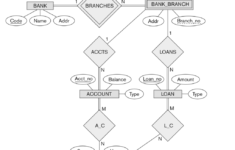
ER Diagram Participation Constraints – The ER Diagram can be a great tool in data mining. It allows you to display complex relationships in a simple format. The fundamentals are the identical regardless of the place you’re working. The first step is to determine “what” your system is. A rectangle is the symbol of the entity and needs to be provided with ample space. Incorporate ovals as characteristics and connect them to the entity. There should be a gap between the rectangle and the oval.
Every single entity on the ER diagram is referred to as an attribute. An attribute is a property, trait, or characteristic that an individual entity has. In the case in an ER diagram the Inventory Item Name is one of the attributes that belongs to the inventory of an entity Item. The entity may possess any number of attributes it requires. Furthermore, each attribute could have its own specific attributes. For instance, a customer’s address could have the following attributes: street number or city. Or state. These are composite attributes, and there are no constraints on the amount of each.
The next stage in the analysis of the ER diagram is to define the amount of information that each entity has. The primary characteristic of every individual is the number of factors that exist across two distinct entities. For instance, a customer can purchase multiple phones from the same cell phone service while the cell provider maintains multiple phones on one bill. The ER diagram can make it easier to identify the connections between entities. Additionally, it will assist you in determining the information that connects the various entities.
When the system is growing and gets more complex and complex, an ER diagram can become more crowded and difficult to understand. The complexity associated with the ER diagram demands a more detailed representation at the micro-level. A well-designed ER diagram will help you comprehend a system in a far more precise manner. It is important to include white space in between tables in your ER diagram to ensure that there is no confusion. If you don’t, it will be difficult to figure out the connection between two entities.
A person is a person. An entity is an object or class. An entity could be an individual as well as a town or even an organization. An entity that is weaker is one that relies on another, and is deficient in the essential characteristics. A characteristic is the property of an object. The person on the ER diagram is an adjective. Similar to the city, it is an entity. Thus, a connection between two entities is an adjective.
The characteristics included in an ER diagram need to be labeled. For instance, a teacher entity may have several value for each subject. A student can be a part of many subjects. The relation between two people is illustrated in the form of diamonds. Usually, these lines are identified by verbs. They are then called entities. If a student has doubts over the meaning of an attribute and is unsure of its meaning, the ER diagram can assist them in understanding the relationship between two objects.